If you’re a property manager or own a private road or other paved surface, you’ll need to decide how to maintain and repair the asphalt. Should you patch the cracks and potholes, or is complete reconstruction a better option?
These decisions can be costly, and you must choose the best option for your situation.
These decisions can be costly, and you must choose the best option for your situation. That is why we here at General Pavement Management put together this quick guide to help you decide which is right for you!
Defining Asphalt Reconstruction & Patching
Asphalt reconstruction is the process of completely removing and replacing existing asphalt. In some cases, this includes the underlying base layers as well. This approach is comprehensive and designed to address severe damage and structural issues.
On the other hand, patching is a localized repair used to fix isolated areas of damaged or failing asphalt (think small potholes, cracks, etc.).While it involves removing and replacing damaged asphalt like reconstruction, it only focuses on the damaged portions, not the entire paved area.
Pros and Cons
Now that we’ve defined our terms, let’s look at the pros and cons of each method.
Asphalt Reconstruction
Pros
1 – Comprehensive Solution<
Reconstruction is a comprehensive solution to failing asphalt. When done correctly, it addresses all issues, and you won’t need to worry about underlying issues causing problems in the future.
2 – Improved Pavement Strength
Reconstructed asphalt is stronger than patched asphalt, especially if the base layers are redone. The reconstructed area will be better equipped to handle heavy traffic loads, weather changes, and other stressors.
3 – Enhanced Longevity
Reconstructed asphalt lasts longer than patched or resurfaced asphalt. While longevity depends on factors like use, maintenance, and weight of traffic, a reconstructed roadway will last up to 25 years. Patching, on the other hand, extends the life of a paved area by only 2-10 years.

4 – Addressing Subgrade Issues
Because reconstruction involves removing all the top layers of asphalt, it lets you address any subgrade issues that exist. While reconstruction doesn’t entail replacing base layers, it allows you to inspect them more closely and make an informed decision.
5 – Opportunity for Design Changes
Since you’re completely reconstructing the asphalt, it’s a great time to make design changes, like adjusting lane widths, adding turning lanes, or improving drainage, to better accommodate traffic flow.
Cons
1 – Higher Cost
Because reconstruction entails the complete removal and replacement of the asphalt, it costs significantly more upfront than other forms of asphalt repair and maintenance.
2 – Takes More Time
Reconstructing asphalt takes a lot longer than less invasive repairs like patching. That means you’ll need to plan how to minimize traffic disruption. For example, if you’re redoing your parking lot, you’ll need to arrange alternative parking.
3 – Environmental Impact
Completely reworking old pavement generates waste materials that negatively impact the environment if handled poorly. Thankfully, recycling is possible in most cases.
Patching
Pros
1 – Cost Effective
Patching is a cost-effective option for dealing with asphalt issues. It allows for targeted repairs, which saves on labor and material costs.
2 – Quick Repairs
Patching is usually a quick, effective fix, depending on the size and extent of the problem. This means you won’t have the same headache of traffic disruption you’d face with reconstruction.
3 – Preventative Maintenance
Quickly patching minor issues prevents them from worsening and causing more extensive problems in the future.
4 – Improved Safety
Patching is a straightforward, affordable way to address parking lot and road safety hazards to keep drivers, pedestrians, and bikers safe.
5 – Localized Solution
If one area of your asphalt is failing, patching allows you to address that issue without replacing the parts that are still in good condition.
Cons
1 – Limited Effectiveness
While patching is great for minor issues, it doesn’t work well for widespread damage or underlying issues. For example, if there is a problem in the base layers of your asphalt, patching will only be a temporary fix.

2 – Less aesthetically pleasing
Patching won’t blend seamlessly into the surrounding asphalt, reducing the visual appeal of the paved area.
3 – Temporary disruption
Patching won’t disrupt traffic as much as reconstruction, but some disruption may still happen depending on the location of the repair. Keep this in mind when scheduling the work.
When is Each One Ideal?
As we’ve established, there are pros and cons to asphalt reconstruction and patching. Which method is best depends entirely on the particular situation.
So when is it best to patch your asphalt?
Patching is ideal in situations of isolated or minimal asphalt damage. If a few cracks are forming or potholes have developed, but the paving seems solid otherwise, patching is the better option. This will extend the life of your pavement, and the upfront cost won’t be as significant.
Asphalt reconstruction is ideal for situations with widespread damage where the asphalt is generally worn out or failing, or the structural base layers have issues. Here are a few problems that indicate reconstruction is best:
- Excessive raveling or oxidation
- Majorly deteriorated topcoat
- Significant cracking, sinkholes, and other signs of subgrade issues
If you’re unsure what’s right for your situation, ask a pavement management expert for advice!
Types of Reconstruction & Patching
There are numerous types of reconstruction and patching available. Let’s take a brief look at a few of the options available in each category.
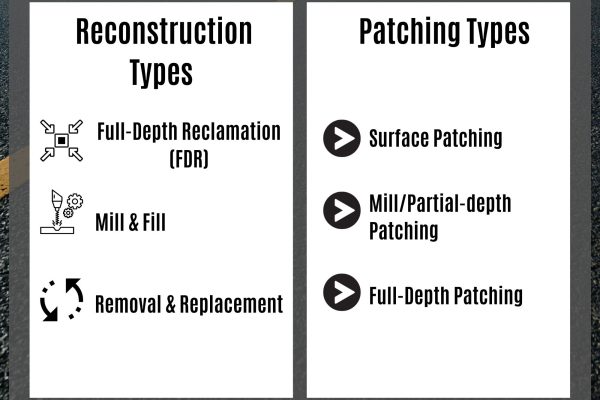
Reconstruction Types
- Full-depth reclamation(FDR): A comprehensive, permanent fix that involves pulverizing the asphalt and its base to create a stabilized base course. Since this involves recycling existing materials, it is considered an environmentally friendly technique.
- Mill and Fill: This consists of removing existing pavement 1-2” deep using a milling machine and installing new asphalt. Mill and fill reconstruction lasts 10-15 years.
- Removal and Replacement: This method is necessary when asphalt reaches the end of its life cycle. It involves the complete removal and replacement of asphalt and sublayers.
Patching Types
- Surface patching: A quick solution for shallow potholes where the base layers are still in great shape. This isn’t meant to be a long-term fix and is best for situations that need immediate resolution.
- Mill or partial-depth patching: Damaged material is milled or removed about 1-2” deep—a good, longer-term solution for shallow potholes and some types of cracks.
- Full-depth patching: This involves removing and replacing the damaged area down to (and sometimes including) the base layers, and is the longest-lasting patch method.
Other Asphalt Maintenance Options
Reconstruction and patching are both good ways to address asphalt issues. However, there are a few other ways to address and prevent problems with your asphalt.
Resurfacing
Resurfacing is just what it sounds like – adding a new layer of asphalt over existing pavement. This approach is good for emergencies and will save money upfront. However, it won’t address underlying issues.
Crack sealing
Crack sealing involves filling asphalt cracks with a water-proof, adhesive sealant. This prevents moisture and debris from entering the cracks and causing further deterioration and can extend the life of pavement for 3-5 years.
Sealcoating
An essential part of asphalt maintenance, sealcoating is a liquid coating that hardens to create a protective seal for the asphalt. It is an economical option that extends the pavement’s lifespan and helps prevent costly repairs. (Learn more about sealcoating in our Guide to Sealcoating.)
Chip Sealing
A cost-effective solution, chip sealing involves applying a layer of liquid asphalt (binder) to the pavement surface, followed by the placement of chips (small stones). The chips are then rolled into the binder to create a durable, skid-resistant surface. Chip sealing helps to seal cracks, waterproof the pavement, and extend its lifespan for moderate-traffic roads. Read more about chip sealing and its benefits!
Asphalt Rejuvenators
Asphalt rejuvenators are chemical additives applied to asphalt surfaces to restore flexibility and improve binding properties. This treatment helps delay the aging process and reduce the formation of cracks.
Cleaning and Debris Removal
Don’t underestimate the importance of keeping your asphalt clean and debris-free! Debris can trap moisture and accelerate pavement deterioration.

How General Pavement Management Can Help
We hope you found this blog helpful as you decide how to effectively maintain your asphalt and deal with the issues that arise.
At General Pavement Management, we offer asphalt paving, grading, concrete, pavement marking, and more! With over 30 years of experience, our team is committed to providing the best experience and the highest quality work possible.
If you have additional questions or need pavement work done, please contact us today!
